|
|
| Line 83: |
Line 83: |
| | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=2e49d72c|size=|date=1993-06-21|source=[[Sega CD 2]] (Sony Model) (NA) (2.11)|comments=MK-4102A MPR-15764-T|quality=|file=MCD2 BIOS US v2.11 930621.7z}} | | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=2e49d72c|size=|date=1993-06-21|source=[[Sega CD 2]] (Sony Model) (NA) (2.11)|comments=MK-4102A MPR-15764-T|quality=|file=MCD2 BIOS US v2.11 930621.7z}} |
| | | | |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=d48c44b5|size=|date=1993-09-07|source=[[Sega CDX]] (NA) (2.21x)|comments=MK-4121 MPR-16139-T|quality=|file=Us cdx 930907.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=d48c44b5|size=|date=1993-09-07|source=[[Sega CDX]] (NA) (2.21x)|comments=MK-4121 MPR-16139-T|quality=|file=CDX BIOS US v2.21 930907.7z}} |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=aacb851e|size=|date=1993-09-16|source=[[Sega Multi-Mega]] (EU) (2.21x)|comments=MK-4121-50 OPR-16140|quality=|file=Eu mmg 930916.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=aacb851e|size=|date=1993-09-16|source=[[Sega Multi-Mega]] (EU) (2.21x)|comments=MK-4121-50 OPR-16140|quality=|file=MultiMega BIOS EU v2.21 930916.7z}} |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=d21fe71d|size=|date=1992-02-06|source=[[Sega Wondermega]] (Japan) (1.00)|comments=HWM-5010 G301|quality=|file=Jp wmg 920206.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=d21fe71d|size=|date=1992-02-06|source=[[Sega Wondermega]] (Japan) (1.00)|comments=HWM-5010 G301|quality=|file=Wondermega BIOS JP v1.00 920206.7z}} |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=2b19972f|size=|date=|source=[[Victor Wondermega M2]] (Japan) (2.00)|comments=RG-M2 G303{{ref|group=n|The ZIP file contains two dumps, a "good" dump and a "bad" dump. The "bad" dump has an incorrect HINT vector, but is otherwise identical to the "good" dump. The CRC32 listed here is for the "good" dump.}}|quality=|file=Wondermega 2.00 Bios.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=2b19972f|size=|date=|source=[[Victor Wondermega M2]] (Japan) (2.00)|comments=RG-M2 G303{{ref|group=n|The ZIP file contains two dumps, a "good" dump and a "bad" dump. The "bad" dump has an incorrect HINT vector, but is otherwise identical to the "good" dump. The CRC32 listed here is for the "good" dump.}}|quality=|file=Wondermega BIOS JP v2.00.7z}} |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=290f8e33|size=|date=1993-12-27|source=[[JVC X-Eye]] (NA) (2.00)|comments=RG-M10BU G304|quality=|file=Us xeye 931227.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=290f8e33|size=|date=1993-12-27|source=[[JVC X-Eye]] (NA) (2.00)|comments=RG-M10BU G304|quality=|file=Xeye BIOS US v2.00 931227.7z}} |
| − | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=12154531|size=|date=|source=[[Aiwa CSD-GM1]] (JP) (2.11)|comments=MPR-15768-T|quality=|file=Aiwa_CSD_GM1_Bios.zip}} | + | {{rom|MCD|sha1=|md5=|crc32=12154531|size=|date=|source=[[Aiwa CSD-GM1]] (JP) (2.11)|comments=MPR-15768-T|quality=|file=AiwaCSD BIOS JP v2.11.7z}} |
| | }} | | }} |
| | | | |
Revision as of 20:52, 26 August 2020
- Back to: Sega Mega-CD.

The original Japanese Mega-CD boot ROM, version 1.00.
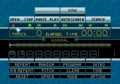
All variants of the Sega Mega-CD come pre-installed with a boot ROM - a menu interface which appears when the console is given power. While a Sega Mega Drive cartridge can boot almost instantaneously, CD-ROMs require verification and loading, which depending on the quality of the disc or drive, can take several seconds. In addition to help drive the CD-ROM, the Mega-CD's boot ROM informs the user that console is in Mega-CD mode, and cruically gives them something more interesting to look at than a blank screen.
Over time, many slightly different boot ROMs were developed by Sega (or its partners), either for localisation purposes, bug fixes or due to changes in hardware. The Wondermega for example has a different style of boot ROM to a standard Mega-CD, while the LaserActive has to accommodate the Mega LD format.
Functions
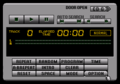
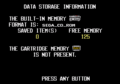
Most Mega-CD boot ROMs offer the same functionality - principly to run Mega-CD games. Most models can also play music CDs and Japanese models accept CD+G discs. As the Mega-CD also contains on-board memory for save games, the boot ROM allows users to manage data, either by removing save data they no longer need, or by transferring it to a CD BackUp RAM Cart. Later boot ROMs and the LaserActive cull some of these features, possibly as a cost-saving measure or limitations with the hardware.
On the Mega-CD, boot ROMs typically play a music track, while colourful Mega-CD and/or Sega logos dance around, demonstrating the system's rotation and scaling abilities. Boot ROM versions 2.00 and later support use of the Sega Mouse in control port 2, should users what to use that device to navigate the menus.
All of these features (and more) were also made available in the Sega Saturn and Sega Dreamcast, as well as most rival disc-based consoles.
Screenshots
Main screen
CD-ROM playback
Storage information
ROM dump status
Notes
- ↑ [The ZIP file contains two dumps, a "good" dump and a "bad" dump. The "bad" dump has an incorrect HINT vector, but is otherwise identical to the "good" dump. The CRC32 listed here is for the "good" dump. The ZIP file contains two dumps, a "good" dump and a "bad" dump. The "bad" dump has an incorrect HINT vector, but is otherwise identical to the "good" dump. The CRC32 listed here is for the "good" dump.]
References