Difference between revisions of "Sega G80"
From Sega Retro
Hyperspeed34 (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| logos= | | logos= | ||
| consoleimage=G80 Arcade.jpg | | consoleimage=G80 Arcade.jpg | ||
| − | |||
| name= | | name= | ||
| maker=[[Sega]] | | maker=[[Sega]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''Sega G80''' is an [[arcade]] system produced by [[Sega]] in 1981. It can be considered a successor to the [[ | + | The '''Sega G80''' is an [[arcade]] system produced by [[Sega]] in 1981. It can be considered a successor to the [[VIC Dual]] system, and was Sega's arcade platform of choice before the release of the [[Sega System 1]]. |
The Sega G80 platform provided a basis for many reasonably successful vector-based games from the company, some of which, such as ''[[Space Fury]]'', ''[[Tac/Scan]]'', and, perhaps most famously, ''[[Star Trek: Strategic Operations Simulator]]'', saw home console/computer ports. | The Sega G80 platform provided a basis for many reasonably successful vector-based games from the company, some of which, such as ''[[Space Fury]]'', ''[[Tac/Scan]]'', and, perhaps most famously, ''[[Star Trek: Strategic Operations Simulator]]'', saw home console/computer ports. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
At the time, Sega sold their products to a network of distributors in the US, who would then sell on to customers. By only selling boards rather than fully assembled cabinets, it was possible for Sega to bypass its distributors after the initial cabinet was sold. It was also noted that a fixed hardware specification could mean games designed for it would appear outdated within months, and thus be harder to sell. | At the time, Sega sold their products to a network of distributors in the US, who would then sell on to customers. By only selling boards rather than fully assembled cabinets, it was possible for Sega to bypass its distributors after the initial cabinet was sold. It was also noted that a fixed hardware specification could mean games designed for it would appear outdated within months, and thus be harder to sell. | ||
| − | Despite assurances from Sega that its current sales model would not change, and that the G80 board could be upgraded, it struggled to convince its distributors | + | Despite assurances from Sega that its current sales model would not change, and that the G80 board could be upgraded, it struggled to convince its distributors, and despite advocating its benefits across 1981 and 1982, found itself releasing games like ''[[Pengo]]'' and ''[[Zaxxon]]'' on bespoke hardware. ''Zaxxon'''s subsequent popularity would undermine the "Convert-a-Game" concept, with Sega's last G80 releasing in 1983. |
| − | + | Sega was not the first company to try and produce a reusable arcade system. In 1980, [[Data East]] released the [[wikipedia:DECO Cassette System|DECO Cassette System]] which would load games from compact cassette, however this system was prone to failure due to the mechanical nature of the system (and the potential for tapes to be demagentised). | |
| − | Sega was not the | + | In hindsight, Sega's analysis was correct, but its solution came to the market too early. Genuine arcade standards would arrive in the years which followed; the JAMMA specifications from 1985/1986 are built around the same idea of swappable arcade PCBs, but do not tie developers down to specific hardware (it is mainly the input and output connectors that are standardised instead, meaning the large cabinets could stay in place). The idea of "swappable games" never went away; [[Nintendo]] would see some success with their "VS" system in 1985, and by the 1990s, the reuse of hardware become necessary for arcade companies to survive, particularly when home consoles became the dominant form of playing video games. |
==Technical specifications== | ==Technical specifications== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:13, 15 May 2024
| |||||||||||||||||
| Sega G80 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer: Sega | |||||||||||||||||
|
The Sega G80 is an arcade system produced by Sega in 1981. It can be considered a successor to the VIC Dual system, and was Sega's arcade platform of choice before the release of the Sega System 1.
The Sega G80 platform provided a basis for many reasonably successful vector-based games from the company, some of which, such as Space Fury, Tac/Scan, and, perhaps most famously, Star Trek: Strategic Operations Simulator, saw home console/computer ports.
Contents
Hardware
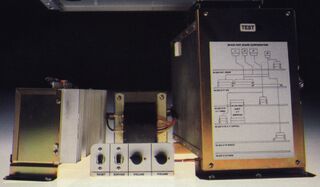
The G80 was designed to be a more versatile system than those seen in arcade cabinets of the past. Rather than rely on bespoke cabinet designs for each game, Sega opted for a more cost-effective "Convert-a-Game" system (as it was marketed in the US), in which games housed on CPU boards could be easily swapped by arcade operators. Announced at Visions '81[2], Sega's plan was to be able to cut install times down to 15 minutes, while also minimising production costs and tackling the poor resale value of used games[2]. As a result, "ConvertaPaks" would cost less to buy than brand new cabinets[3] (about $1,000 USD each[1], versus the $3,000 Sega estimated the average arcade game to cost in 1981[4]).
The G80 system consists of a card cage with a 6 slot backplane that can be populated in different game configurations from a selection of 10+ different pluggable boards, allowing it to be configured as either a raster system if a raster video board is inserted, or a vector system that can display color vector graphics (or X/Y "Colorbeam" games, as Sega called them at the time).
The G80 gets its name from its Z80 CPU which was coupled with a custom security chip to prevent operators from abusing the swappable system. The security chip would obfuscate the "ld (address),a" instruction (opcode 32h) differently based on the security chip installed — an early form of copy protection. The mangling algorithms are rather complicated, and differ from security chip to security chip.[5]
History
Space Odyssey was the first game to use the G80 system, followed by Space Fury[2].
For a while, Sega believed the "Convert-a-Game" concept was the future. David Rosen predicted that improvements in microprocessor technology would mean players would be constantly seeking new experiences, and as a result, arcade operators would have to keep changing their lineup of games; a business strategy that would not be economically viable if entirely new systems had to be purchased from manufacturers (who in turn relied on these new sales to stay in business)[6].
At the time, Sega sold their products to a network of distributors in the US, who would then sell on to customers. By only selling boards rather than fully assembled cabinets, it was possible for Sega to bypass its distributors after the initial cabinet was sold. It was also noted that a fixed hardware specification could mean games designed for it would appear outdated within months, and thus be harder to sell.
Despite assurances from Sega that its current sales model would not change, and that the G80 board could be upgraded, it struggled to convince its distributors, and despite advocating its benefits across 1981 and 1982, found itself releasing games like Pengo and Zaxxon on bespoke hardware. Zaxxon's subsequent popularity would undermine the "Convert-a-Game" concept, with Sega's last G80 releasing in 1983.
Sega was not the first company to try and produce a reusable arcade system. In 1980, Data East released the DECO Cassette System which would load games from compact cassette, however this system was prone to failure due to the mechanical nature of the system (and the potential for tapes to be demagentised).
In hindsight, Sega's analysis was correct, but its solution came to the market too early. Genuine arcade standards would arrive in the years which followed; the JAMMA specifications from 1985/1986 are built around the same idea of swappable arcade PCBs, but do not tie developers down to specific hardware (it is mainly the input and output connectors that are standardised instead, meaning the large cabinets could stay in place). The idea of "swappable games" never went away; Nintendo would see some success with their "VS" system in 1985, and by the 1990s, the reuse of hardware become necessary for arcade companies to survive, particularly when home consoles became the dominant form of playing video games.
Technical specifications
- Sega USB (Universal Sound Board)[8]
- MCU: Intel i8035 @ 3.12 MHz (8-bit instructions, 3.12 MIPS, 1 instruction per cycle)
- Sound chip: Sega Melody Generator (programmable sound generator)
- Speech Board (optional)
- MCU: Intel i8035/i8039 @ 3.12 MHz (8-bit instructions, 3.12 MIPS)
- Speech synthesizer: General Instrument SP0250 (linear predictive coding)
- Sega System 1 sound board (optional, used for Sindbad Mystery in 1983)
- Sound chips: Sega SN76496 @ 4 MHz, Sega SN76496 @ 2 MHz
- Raster graphics board: Sega Video I[5]
- Raster display controller: Sega Raster Display Controller @ 15.468 MHz
- Video resolution:
- Horizontal: 256×224 (display), 328×262 (overscan)
- Vertical: 224×256 (display), 262×328 (overscan)[9]
- Color palette table: 256 (8-bit RGB PROM)
- Colors on screen: 64 to 128 (palette RAM)
- Tilemap planes: 2 layers, horizontal and vertical scrolling,[9] 8×8 tiles, 4 colors per tile
- Sprite capabilities: 28 to 32 sprites per scanline, 224 to 256 sprite pixels/texels per scanline, 4 colors per sprite, 8×8 to 16×16 sizes[7]
- Vector display controller: Sega Display Controller[10]
- Color depth: 64 (6-bit RGB)[11]
List of games
Raster
- 005 (1981)
- Astro Blaster (1981)
- Space Odyssey (1981)
- Monster Bash (1982)
- Pig Newton (1983)
- Sindbad Mystery (1983)
Vector
- Space Fury (1981)
- Eliminator (1981)
- Battle Star (1982)
- Star Trek: Strategic Operations Simulator (1982)
- Tac/Scan (1982)
- Zektor (1982)
Promotional material
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 File:ConvertaGames Arcade US Flyer.pdf, page 2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Cash Box, "July 4, 1981 (Part 2 of 2)" (US; 1981-07-04), page 57
- ↑ Cash Box, "July 4, 1981 (Part 2 of 2)" (US; 1981-07-04), page 58
- ↑ File:ConvertaGame Arcade US Flyer.pdf, page 2
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Sega G-80 raster hardware (MAME)
- ↑ Cash Box, "December 26, 1981" (US; 1981-12-26), page 84
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Sega G80 Hardware Reference (1997-10-25)
- ↑ Data Bus, "March 1983: Volume 4, Number 1" (US; 1983-03-xx), page 2
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Sega G-80 raster video hardware (MAME)
- ↑ Sega G-80 vector hardware (MAME)
- ↑ Sega G-80 vector video hardware (MAME)
| Sega arcade boards |
|---|
| Originating in arcades |
|
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
| Console-based hardware |
|
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
|
| PC-based hardware |
|
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|

