Difference between revisions of "Sega System 1"
From Sega Retro
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
* [[Sprite]] plane: Line buffer, double buffering, 32 sprites per scanline, 16 colors per sprite, sprite flipping, hardware collision detection{{ref|https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/video/system1.cpp}}{{ref|https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/drivers/system1.cpp}} | * [[Sprite]] plane: Line buffer, double buffering, 32 sprites per scanline, 16 colors per sprite, sprite flipping, hardware collision detection{{ref|https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/video/system1.cpp}}{{ref|https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/drivers/system1.cpp}} | ||
** Sprite sizes: 8 to 256 pixels width, 8 to 256 pixels height | ** Sprite sizes: 8 to 256 pixels width, 8 to 256 pixels height | ||
| − | ** Pixel clock | + | ** [[Pixel]] clock rate: 10 MHz |
| − | ** [[Fillrate]]: 10 [[Pixel|MPixels/s]], 166,402 | + | ** [[Fillrate]]: 10 [[Pixel|MPixels/s]], 166,402 pixels per frame, 640 [[texel]]s per scanline |
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 02:51, 4 October 2016
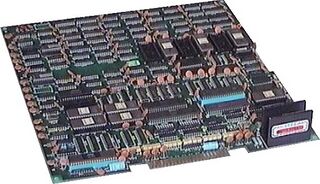
| |||||
| Sega System 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer: Sega | |||||
|
The Sega System 1 is an arcade platform introduced by Sega in 1983,[1] based on earlier 1982 prototype hardware. It is a Z80-based platform and the first in the decade-long "System" series of arcade boards.
The System 1 was a relatively popular arcade board for its day, supported not only by Sega, but by Japanese developers Coreland and VIC Tokai between 1983 and 1987. In 1985 it was succeeded by the slightly more powerful Sega System 2 board, though new games were released for both systems concurrently. Many of the System 1's games were ported to the SG-1000 and Sega Master System consoles.
Specifications
- Board composition: One board
- Main CPU: Zilog Z80 @ 4 MHz (8-bit & 16-bit instructions @ 0.58 MIPS)
- Sound CPU: Zilog Z80 @ 4 MHz (8-bit & 16-bit instructions @ 0.58 MIPS)
- Sound chips: Sega SN76496 @ 4 MHz, Sega SN76496 @ 2 MHz
- GPU chipset:[2]
- Sega 315-5011 sprite line comparator
- Sega 315-5012 sprite generator
- Sega 315-5049 tilemap chip
- MCU: Intel 8751[3]
- RAM: 82 KB[3]
- Main: 4 KB
- Video: 12 KB (4 KB video, 2 KB sprites, 2 KB palette, 4 KB collision)
- Sound: 2 KB
- MCU: 64 KB
- Video resolution: 256×224 (display), 640×260 (overscan)[2]
- Refresh rate: 60.0952 Hz (V-sync)
- Color palette: 4096[4]
- Colors on screen: 2048[2]
- Tilemap planes: 2 background layers (1 static, 1 scrolling), 8×8 tiles[4][2]
- Tilemap sizes: 256×256 for both planes
- Sprite plane: Line buffer, double buffering, 32 sprites per scanline, 16 colors per sprite, sprite flipping, hardware collision detection[4][2]
Prototype
Super Locomotive in 1982 ran on prototype arcade hardware that was very similar to the Sega System 1 later released in 1983. Super Locomotive included the following technical specifications:[5][6][7]
- Main CPU: Zilog Z80 @ 4 MHz (8/16-bit instructions, 1.16 MIPS)
- Audio CPU: Zilog Z80 @ 4 MHz (8/16-bit instructions, 1.16 MIPS)
- Sound chips: SN76496 @ 4 MHz, SN76496 @ 2 MHz
- Graphics chipset: Sega 315-5011 (sprite line comparator), Sega 315-5012 (sprite generator)
- Display resolution: 248×224
- Overscan resolution: 256×256
- Refresh rate: 60 Hz
- Frame rate: 60 FPS
- Color palette table: 1568
- Colors on screen: 768
- Sprites:
- Background planes: 2 tilemap layers
Gallery
List of Games
- Super Locomotive (1982)
- Regulus (1983)
- Star Jacker (1983)
- Up'n Down (1983)
- Bull Fight (1984)
- Flicky (1984)
- Mister Viking (1984)
- Spatter (1984)
- SWAT (1984)
- Water Match (1984)
- 4D Warriors (1985)
- Choplifter (1985)
- I'm Sorry (1985)
- My Hero (1985)
- Pitfall II (1985)
- Sega Ninja (1985)
- Teddy Boy Blues (1985)
- Brain (1986)
- Gardia (1986)
- Noboranka (1986)
- Rafflesia (1986)
- Wonder Boy (also released on Sega System 2) (1986)
- Wonder Boy Deluxe (1986)
- Block Gal (1987)
References
- ↑ http://sega.jp/fb/segahard/sc3000/gallery.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/drivers/system1.cpp
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 https://github.com/mamedev/mame/blob/master/src/mame/drivers/system1.cpp
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 https://github.com/mamedev/mame/tree/master/src/mame/video/system1.cpp
- ↑ Super Locomotive (MAME)
- ↑ Super Locomotive video hardware (MAME)
- ↑ Sega Z80 Based Hardware (System 16)
| Sega arcade boards |
|---|
| Originating in arcades |
|
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
| Console-based hardware |
|
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
|
| PC-based hardware |
|
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|

