Difference between revisions of "Sega Dreamcast"
From Sega Retro
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
A list of names, likely the various people involved with console's creation, can be found at '''0x1A1A0''' in the flash ROM. | A list of names, likely the various people involved with console's creation, can be found at '''0x1A1A0''' in the flash ROM. | ||
{{creditstable| | {{creditstable| | ||
| − | *[[Shoichiro Irimajiri]], [[Sadahiko Hirose]], [[Hidekazu Yukawa]], [[Hideki Satou]], [[Nobuhisa Yamada]], [[Taku Matsubara]], [[Kazuhiro Yasutomi]], [[Shoji Nishikawa]], [[Takashi Sekimoto]], [[Toshihiro Oba]], [[Shuji Hori]], [[Masaharu Shinohara]], [[Kazuhiro Baba]], [[Katsunori Gendo]], [[Kouji Horikawa]], [[Masatoshi Horikawa]], [[Osamu Hosokawa]], [[Seiichi Kajiwara]], [[Junko Kase]], [[Toshikazu Kawada]], [[Yasuhisa Kawase]], [[Yusuke Kiguchi]], [[Naohiko Kobayashi]], [[Manabu Kubo]], [[Teruaki Kuwana]], [[Kunihiro Mori]], [[Tomoyuki Mori]], [[Shigeru Motoyoshi]], [[Takeshi Nagashima]], [[Yoshifumi Nakamura]], [[Chuji Nakayama]], [[Madoka Nakayama]], [[Tatsuya Namatame]], [[Yasuhiro Nishiyama]], [[Toshiyuki Ogawa]], [[Tadashi Ohya]], [[Tetsuya Okawa]], [[Tatsuya Sakurai]], [[Hideaki Satou]], [[Yutaka Suetsugi]], [[Eriko Suzuki]], [[Masahiko Takeuchi]], [[Makoto Takiguchi]], [[Ryo Taki]], [[Masaki Tanaka]], [[Kazuo Tsuda]], [[Satoshi Tsuda]], [[Koichi Takayasu]], [[Naoki Niizuma]], [[Atsunori Himoto]], [[Tomoe Shinohara]], [[Kunihiro Tokumaru]], [[Yoshikazu Nagao]], [[Satoshi Kira]], [[Akitoshi Oikawa]], [[Hirokazu Hama]], [[Toshimichi Sugai]], [[Naoji Ozaki]], [[Hiroki Goto|Hiroki Gotou]], [[Masaharu Yoshii]], [[Masaki Kawahori]], [[Yuki Yamanaka]], [[Shinichi Uchida]], [[Masahiro Seki]], [[Takashi Ando]], [[Hideki Kudo]], [[Nobuhiro Fukuda]], [[Jiro Terakawa]], [[Yoichi Uchida]], [[Hiroki Okabata]], [[Kazuyoshi Hara]], [[Yuko Nasu]], [[Syuuji Okada]], [[Yutaka Okunoki]], [[Tatsuya Kouzaki|Tatuya Kouzaki]], [[Tadashi Jokagi]], [[Yoshiaki Kashima]], [[Kazumi Suyama]], [[Yutaka Sugano]], [[Tomoko Hasegawa]], [[Kazuhiro Matsuta]], [[Katsuhiko Sato]], [[Manabu Kusunoki]], [[Shinichi Oya]], [[Takeshi Suzuki]], [[Kazunori Shibata]], [[Shigeyuki Shimizu]], [[Masayuki Imanishi]], [[Kenji Ohtsuji]], [[Masamichi Miyoshi]], [[Tarou Mitani]], [[Takaaki Jindou]], [[Yoshitake Noguchi]] | + | *[[Shoichiro Irimajiri]], [[Sadahiko Hirose]], [[Hidekazu Yukawa]], [[Hideki Satou]], [[Nobuhisa Yamada]], [[Taku Matsubara]], [[Kazuhiro Yasutomi]], [[Shoji Nishikawa]], [[Takashi Sekimoto]], [[Toshihiro Oba]], [[Shuji Hori]], [[Masaharu Shinohara]], [[Kazuhiro Baba]], [[Katsunori Gendo]], [[Kouji Horikawa]], [[Masatoshi Horikawa]], [[Osamu Hosokawa]], [[Seiichi Kajiwara]], [[Junko Kase]], [[Toshikazu Kawada]], [[Yasuhisa Kawase]], [[Yusuke Kiguchi]], [[Naohiko Kobayashi]], [[Manabu Kubo]], [[Teruaki Kuwana]], [[Kunihiro Mori]], [[Tomoyuki Mori]], [[Shigeru Motoyoshi]], [[Takeshi Nagashima]], [[Yoshifumi Nakamura]], [[Chuji Nakayama]], [[Madoka Nakayama]], [[Tatsuya Namatame]], [[Yasuhiro Nishiyama]], [[Toshiyuki Ogawa]], [[Tadashi Ohya]], [[Tetsuya Okawa]], [[Tatsuya Sakurai]], [[Hideaki Satou]], [[Yutaka Suetsugi]], [[Eriko Suzuki]], [[Masahiko Takeuchi]], [[Makoto Takiguchi]], [[Ryo Taki]], [[Masaki Tanaka]], [[Kazuo Tsuda]], [[Satoshi Tsuda]], [[Koichi Takayasu]], [[Naoki Niizuma]], [[Atsunori Himoto]], [[Tomoe Shinohara]], [[Kunihiro Tokumaru]], [[Yoshikazu Nagao]], [[Satoshi Kira]], [[Akitoshi Oikawa]], [[Hirokazu Hama]], [[Toshimichi Sugai]], [[Naoji Ozaki]], [[Hiroki Goto|Hiroki Gotou]], [[Masaharu Yoshii]], [[Masaki Kawahori]], [[Yuki Yamanaka]], [[Shinichi Uchida]], [[Masahiro Seki]], [[Takashi Ando]], [[Hideki Kudo]], [[Nobuhiro Fukuda]], [[Jiro Terakawa]], [[Yoichi Uchida]], [[Hiroki Okabata]], [[Kazuyoshi Hara]], [[Yuko Nasu]], [[Syuuji Okada]], [[Yutaka Okunoki]], [[Tatsuya Kouzaki|Tatuya Kouzaki]], [[Tadashi Jokagi]], [[Yoshiaki Kashima]], [[Kazumi Suyama]], [[Yutaka Sugano]], [[Tomoko Hasegawa]], [[Kazuhiro Matsuta]], [[Katsuhiko Sato]], [[Manabu Kusunoki]], [[Shinichi Oya]], [[Takeshi Suzuki]], [[Kazunori Shibata]], [[Shigeyuki Shimizu]], [[Masayuki Imanishi]], [[Kenji Otsuji|Kenji Ohtsuji]], [[Masamichi Miyoshi]], [[Tarou Mitani]], [[Takaaki Jindou]], [[Yoshitake Noguchi]] |
| source=ROM text{{ref|https://tcrf.net/Dreamcast}} | | source=ROM text{{ref|https://tcrf.net/Dreamcast}} | ||
| console=DC | | console=DC | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
==Magazine articles== | ==Magazine articles== | ||
{{mainArticle|{{PAGENAME}}/Magazine articles}} | {{mainArticle|{{PAGENAME}}/Magazine articles}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video coverage== | ||
| + | {{mainArticle|{{PAGENAME}}/Video coverage}} | ||
==Promotional material== | ==Promotional material== | ||
Revision as of 15:21, 1 January 2024

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dreamcast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer: Sega | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants: Sega NAOMI, Atomiswave, Sega System SP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Dreamcast (ドリームキャスト) is a home video game console manufactured by Sega as a successor to the Sega Saturn. Dubbed as Sega's "Super Console"[12], it is a "128-bit" machine designed with then-cutting edge hardware and a focus on the internet. The Dreamcast was originally released in Japan in November 1998 before seeing a Western release the following year.
The Dreamcast was Sega's seventh and final home video game console, and was discontinued in early 2001[13][14] due to financial constraints within the company. It had sold at least 8.2 million hardware units and 51.63 million software units by March 2001,[15], with estimates suggesting 10.6 million hardware units in total.
An arcade counterpart to the Dreamcast exists as the Sega NAOMI.
Hardware
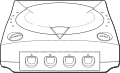
The Dreamcast is a small, white box with aesthetics designed to appeal to a wide-ranging audience. It was envisioned as an "128-bit" "super console", designed to leapfrog "32-bit" and "64-bit" contemporaries in the form of the PlayStation and Nintendo 64, respectively (although from a technical standpoint, its main processor deals in 32-bit or 64-bit instructions, with the 128-bit figure coming from the graphics hardware). Incidentally the Dreamcast was the last home console to use "bits" as a selling point, with processing capabilities now typically measured in other ways.
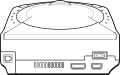
Taking design cues from the Nintendo 64 and the Sega Saturn, the Dreamcast contains four control ports, a removable modem, disc drive and an extension port (as well as the expected AV and power inputs). It is not backwards compatible with any prior Sega hardware or software (although its controller derives from the Saturn's 3D Control Pad), and operates in much the same way as the Saturn (and PlayStation) does, with a configurable settings and memory management accessed through a BIOS screen.
The Dreamcast uses a proprietary format of storage called GD-ROMs for games in order to circumvent software piracy, a strategy that ultimately backfired when the first run of discs had a high rate of defects. The format was also cracked fairly quickly (and in some cases, the pirated games were released before the legitimate versions). Sega largely had themselves to blame for the high levels of Dreamcast piracy—their use of the GD-ROM format was completely undermined by the console's support for the Mil-CD format, which allowed the console to boot from a standard CD-R. Mil-CD support was removed from the final Dreamcast revisions toward the end of the console's life.
The GD-ROM format also put the console at a disadvantage when competing against the PlayStation 2 - the PS2 used DVDs, and could therefore run DVD videos making it an inexpensive DVD player as well as a video game console. DVD-ROMs also have more storage space, allowing for bigger games (though the initial run of PS2 games used a blue CD-ROM format). Sega looked into DVD technology during the Dreamcast's development but claimed it was too expensive.
The Dreamcast was the first video game console to ship with a built-in 56k modem, with broadband adapters being made available later on in certain regions. This allowed the system to connect to the internet using a custom, fully-functional web browser and e-mail client. Many games released for the Dreamcast shipped with online play modes, the most popular being Phantasy Star Online and the Sega Sports lineup (now published under the ESPN label). Although other consoles before the Dreamcast had network gaming support, such as the Sega Saturn's NetLink and the Sega Mega Drive's XB∀ND, the Dreamcast was the first game console to include this ability out of the box and is therefore considered the first internet-enabled home game system.
The Dreamcast has a modest hacking enthusiast community. The availability of Windows CE software development kits on the Internet—as well as ports of Linux (LinuxDC) and dreamcast NetBSD operating systems to the Dreamcast—gave programmers a selection of familiar development tools to work with, even though they do not really support the high speed graphics. A homebrew minimal operating system called Kallistios offers support for most hardware, while not offering multi-tasking, which is superfluous for games. Many emulators and other tools (MP3, DivX players, and image viewers) have been ported to or written for the console, taking advantage of the relative ease with which a home user can write a CD which is bootable by an unmodified Dreamcast.
Sega released an arcade board, using the same technology as the Dreamcast, called Sega NAOMI, leading to many Dreamcast-exclusive games with a high level of arcade quality.
The Dreamcast's PowerVR CLX2 was the first GPU for a home system with hardware capabilities such as bump mapping, volumetric effects,[16] order-independent transparency, and Dot3 normal mapping.[17]
Models
- Main article: Dreamcast consoles.
Japanese Dreamcasts can be identified by the triangle at the front of the unit. Though the power LED is identical across all regions, the piece of plastic attached to the lid of the Japanese model is transparent, while in North America it is grey. The Japanese models also have the text "Designed for Microsoft Windows CE" printed on the front right, whereas Western versions say "Compatible with Microsoft Windows CE".
For a full list of special edition Dreamcasts, see Special Dreamcast Models.
Technical specifications
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast/Technical specifications.
Hardware comparisons
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast/Hardware comparison.
History
- Main article: History of the Sega Dreamcast.
Localised names
| Language | Localised Name | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| English | Sega Dreamcast | Sega Dreamcast |
| Japanese | ドリームキャスト | Dreamcast |
| Hebrew | דרימקאסט |
Games
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast games.
Production credits
A list of names, likely the various people involved with console's creation, can be found at 0x1A1A0 in the flash ROM.
- Shoichiro Irimajiri, Sadahiko Hirose, Hidekazu Yukawa, Hideki Satou, Nobuhisa Yamada, Taku Matsubara, Kazuhiro Yasutomi, Shoji Nishikawa, Takashi Sekimoto, Toshihiro Oba, Shuji Hori, Masaharu Shinohara, Kazuhiro Baba, Katsunori Gendo, Kouji Horikawa, Masatoshi Horikawa, Osamu Hosokawa, Seiichi Kajiwara, Junko Kase, Toshikazu Kawada, Yasuhisa Kawase, Yusuke Kiguchi, Naohiko Kobayashi, Manabu Kubo, Teruaki Kuwana, Kunihiro Mori, Tomoyuki Mori, Shigeru Motoyoshi, Takeshi Nagashima, Yoshifumi Nakamura, Chuji Nakayama, Madoka Nakayama, Tatsuya Namatame, Yasuhiro Nishiyama, Toshiyuki Ogawa, Tadashi Ohya, Tetsuya Okawa, Tatsuya Sakurai, Hideaki Satou, Yutaka Suetsugi, Eriko Suzuki, Masahiko Takeuchi, Makoto Takiguchi, Ryo Taki, Masaki Tanaka, Kazuo Tsuda, Satoshi Tsuda, Koichi Takayasu, Naoki Niizuma, Atsunori Himoto, Tomoe Shinohara, Kunihiro Tokumaru, Yoshikazu Nagao, Satoshi Kira, Akitoshi Oikawa, Hirokazu Hama, Toshimichi Sugai, Naoji Ozaki, Hiroki Gotou, Masaharu Yoshii, Masaki Kawahori, Yuki Yamanaka, Shinichi Uchida, Masahiro Seki, Takashi Ando, Hideki Kudo, Nobuhiro Fukuda, Jiro Terakawa, Yoichi Uchida, Hiroki Okabata, Kazuyoshi Hara, Yuko Nasu, Syuuji Okada, Yutaka Okunoki, Tatuya Kouzaki, Tadashi Jokagi, Yoshiaki Kashima, Kazumi Suyama, Yutaka Sugano, Tomoko Hasegawa, Kazuhiro Matsuta, Katsuhiko Sato, Manabu Kusunoki, Shinichi Oya, Takeshi Suzuki, Kazunori Shibata, Shigeyuki Shimizu, Masayuki Imanishi, Kenji Ohtsuji, Masamichi Miyoshi, Tarou Mitani, Takaaki Jindou, Yoshitake Noguchi
- Hideki Sato
- Hiroyuki Ohtaka
- Start-up Video Production: Kazuhiro Fumoto
- Start-up Jingle: Ryuichi Sakamoto
Magazine articles
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast/Magazine articles.
Video coverage
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast/Video coverage.
Promotional material
- Main article: Sega Dreamcast/Promotional material.
Digital manuals
Gallery
| Sega Retro Average | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| 74 | |
|---|---|
| Based on 6 reviews | |
Official photographs
Logos by regions
| Logo | Region |
|---|---|
| Used in Japan, Asia and South Korea | |
| Used in North and South America | |
| Used in Western and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, Australasia |
Artwork
Patents
External links
- www.dreamcast.com.au (Australia and New Zealand)
- www.sega.at (Austria)
- dreamcast.gz.ee (Estonia)
- www.dreamcast-europe.com (Europe)
- www.dcfin.net (Finland)
- dreamcastfinland.net (Finland)
- segadc.uw.hu (Hungary)
- www.dreamcast.is (Iceland)
- dreamcast.times.lv (Latvia)
- dreamarena.ru (Russia)
- www.dreamcast.pl (Poland)
- dreamcast-rus.boom.ru (Russia)
- dream-cast.narod.ru (Russia)
- dreamcast.miesto.sk (Slovakia)
- www.dreamcast.nu (Sweden)
References
- ↑ Press release: 1999-09-02: Sega Dreamcast Launch Titles and Peripherals
- ↑ Computer & Video Games, "November 1999" (UK; 1999-10-13), page 52
- ↑ Computer & Video Games, "October 1999" (UK; 1999-09-15), page 59
- ↑ File:ConsolesMicro FR 01.pdf, page 15
- ↑ File:NextLevel DE 1999-0910.pdf, page 6
- ↑ Hyper, "September 1999" (AU; 1999-xx-xx), page 29
- ↑ Dreamcast (Tectoy) (Wayback Machine: 2000-03-03 16:07)
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20010409225930/http://sega.ru:80/news.phtml
- ↑ https://www.idnes.cz/ekonomika/test-a-spotrebitel/nova-konzole-dreamcast-prehrava-konkurenci.A_2000M051T05A
- ↑ https://www.ign.com/articles/2000/11/22/dreamcast-heads-to-india
- ↑ https://www.afaqs.com/news/story/795_Stracon-ready-to-turn-the-TV-into-a-multi-dimensional-entertainment-device
- ↑ Press release: 1998-05-21: Sega Unveils Super Console!
- ↑ Press Release: 2001-01-28: Dúvidas e confirmações no futuro da Dreamcast
- ↑ Press Release: 2001-10-29: Dreamcast não desiste e mostra novos trunfos
- ↑ File:AnnualReport2001 English.pdf, page 16
- ↑ Gamers' Republic, "August 1998" (US; 1998-07-21), page 29
- ↑ [PC Magazine, December 1999, page 193 PC Magazine, December 1999, page 193]
- ↑ The Cutting Room Floor: Dreamcast
- ↑ File:Sega_Consumer_History_JP_EnterBrain_Book.pdf, page 23
- ↑ https://www.facebook.com/hiroyuki.ohtaka/about_work_and_education
- ↑ https://area.autodesk.jp/column/tutorial/softimage_maniacs/ (Wayback Machine: 2023-10-29 15:09)
- ↑ JW Szczepaniak (2014). The Untold History of Japanese Game Developers: Volume 1
- ↑ GameZine (UK) (+0:00)
- ↑ Komputer Świat Gry, "Czerwiec-lipiec 2000" (PL; 2000-xx-xx), page 72
- ↑ Man!ak, "Grudzień 1999" (PL; 1999-xx-xx), page 10
- ↑ Play, "Wszystko o Konsolach" (PL; 2001-xx-xx), page 2
- ↑ PSX Extreme, "02/99" (PL; 1999-0x-xx), page 18
- ↑ PSX Extreme, "03/2001" (PL; 2001-0x-xx), page 42
| Sega Home Video Game Systems | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG-1000 | SG-1000 II | Mega Drive | Mega Drive II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SC-3000 | Mega-CD | Mega-CD II | Genesis 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sega Mark III | 32X | Dreamcast | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Master System | Master System II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AI Computer | Game Gear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturn | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pico | Beena | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- JP Dreamcast hardware
- US Dreamcast hardware
- DE Dreamcast hardware
- ES Dreamcast hardware
- FR Dreamcast hardware
- UK Dreamcast hardware
- CZ Dreamcast hardware
- PL Dreamcast hardware
- RU Dreamcast hardware
- AU Dreamcast hardware
- BR Dreamcast hardware
- MA Dreamcast hardware
- IN Dreamcast hardware
- KR Dreamcast hardware
- AS Dreamcast hardware
- Dreamcast hardware
- Credits without reference
- Sega Dreamcast